

The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. If you have no moving coil instrument available, it is of course also possible to replace M1 with a digital meter. The purpose of S1 is to reverse the polarity: the upper position drawn is for NPN transistors, the bottom for PNP types. It will be clear that position 2 of S3 is intended for high gains of up to 1000 and position 3 for gains of 0 to 100. In position 3 the base resistor is 10 times lower (R1 = 56 kΩ), so in this case the reading has to be multiplied by 10 to obtain the gain. Therefore, the value indicated by the meter, when S3 is in position 2, has to be multiplied by a factor of 100 to obtain the gain of the transistor. If the transistor has a gain of 1000 it will cause a collector current (and therefore a meter current) of 10mA, causing full-scale deflection of the moving coil instrument. The circuit works on 3V DC, derived using a zener diode in conjunction with a step-down. The circuit could even be used for checking of PNP and NPN transistors. This is a very simple circuit which can be used for testing of SCRs as well as triacs. With S3 in position 2 this will be (6 V – 0.6 V)/560 kΩ = approx. This is the circuit diagram of TRIAC, SCR and Transistor tester. When a transistor is being tested (S2 open, S3 in position 2 or 3) a current will flow through the base-emitter junction of the transistor under test, the value of which can be computed by dividing the voltage across R1 or R2 by its resistance. A current of 10mA will flow, resulting in full-scale deflection of the meter.
#Transistor tester diagram series
The operation is simple: in the position ‘battery test’ (S2 closed), the 10mA moving coil meter M1 in series with a 600 Ω resistor (R4 + R5) is connected to a 6 V battery.
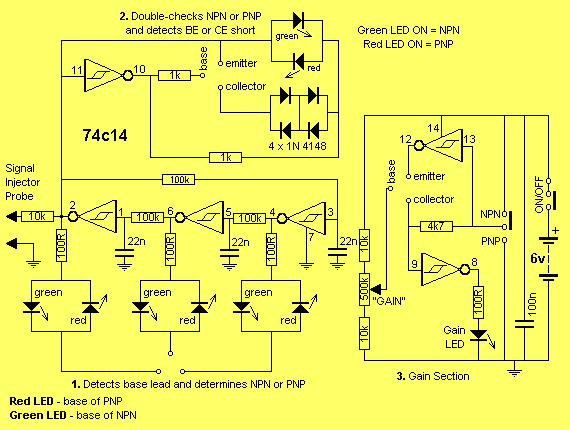
The circuit has been designed only to quickly carry out a brief check, when there is no time or equipment to carry out a thorough test. This is about the simplest conceivable test circuit, so don’t expect super accuracy. This tester is intended to quickly check whether a transistor is functional or not and possibly also select two or more transistors with (approximately) equal gains.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
